Volume 7 Number 2
©The Author(s) 2005
Reconstructing Teacher Education to Prepare Qualified Preschool Teachers: Lessons from New Jersey
Abstract
New Jersey provides a unique context from which to explore the issue of preschool teacher certification and preparation because of the 1998 and 2000 Supreme Court decisions related to the Abbott districts. These decisions ruled that the 30 poorest districts were to create systems of high-quality preschool for all 3- and 4-year-old children beginning in the 1999-2000 school year. This paper reports on the state's efforts to create a new system of preschool teacher certification and explores how current practices compare to national standards for the content and capacity of high-quality teacher preparation. The findings from this study indicate that it is possible, in a relatively short period of time, to put in place a system of early childhood teacher preparation that has the capacity to upgrade the credentials of the state's workforce. Lessons from this case suggest that policy makers and teacher educators must focus on the coordination of human and financial resources to ensure equity and quality of teacher education programs.
Introduction
It is now widely recognized that qualified teachers are an essential component of preschool programs that result in improved outcomes for young children (Barnett, 2003; Whitebook, 2003). Children who are educated by teachers with both a bachelor's degree and specialized training in child development and early education have been found to be more sociable, exhibit a more developed use of language, and perform at a higher level on cognitive tasks than children who are cared for by less-qualified adults (Bowman, Donovan, & Burns, 2001; Dwyer, Chait, & McKee, 2000; Howes, 1997). This research base, along with the evidence attesting to the long-term impacts of high-quality preschool programs on children's social and academic success (Barnett, 1998; Campbell, Pungello, Miller-Johnson, Burchinal, & Ramey, 2001), has contributed to an increased demand for qualified preschool teachers. As one report states, "High quality ECE teachers are essential for addressing pervasive and persistent educational problems such as low reading and math achievement, particularly of children from low socioeconomic circumstances" (American Association for Colleges of Teacher Education Focus Council on Early Childhood Education, 2004, p. 3).
Despite this demand, the wide variation in state regulations regarding the baseline of education needed to be a preschool teacher (Ackerman, 2004) has resulted in a potential shortage of such teachers. Nationally representative studies of the early childhood workforce (Saluja, Early, & Clifford, 2002) estimate that only 50% of the approximately 284,277 preschool teachers currently working in the United States have a bachelor's degree of some kind, and many of them do not have a teaching credential. Moreover, even if teachers do have a teaching certificate, they may not have had the specialized training that is critical to being a knowledgeable early childhood professional (Saluja, Early, & Clifford, 2002). For example, it has been argued that most early childhood teacher preparation programs tend to convey outdated child development knowledge; therefore, early childhood teachers often underestimate the competence of young children (Bowman, Donovan, & Burns, 2001).
With the ongoing growth of publicly funded preschool programs and the use of existing child care and Head Start programs as part of many state efforts, it is becoming increasingly necessary to both upgrade the qualifications of teachers currently working in classrooms as well as induct new members to the field through teacher preparation programs. However, little research attention has been given to what is needed to create a system of early childhood teacher education that prepares teachers, many of whom are nontraditional students, to work effectively with diverse groupings of students so that they enter school ready to learn. This paper reports on one state's efforts to create a new system of preschool teacher certification and explores how current practices compare to national standards for the content and capacity of high-quality teacher preparation. What was learned through the process of reforming early childhood teacher preparation in New Jersey offers insights for other states and programs that are attempting to address the challenges of creating a qualified and knowledgeable preschool teaching workforce.
High-Quality Early Childhood Teacher Preparation
The world of early childhood teacher preparation, in general, is under-researched, and little available evidence exists to inform practice (Bredekamp, 1996; Horm-Wingerd, Hyson, & Karp, 2000). It has been argued therefore that many teacher education programs are based more on ideology than on what is known about effective curriculum and pedagogy (Isenberg, 2000). The quality of any teacher preparation program tends to be characterized by two interrelated factors—the content of the curriculum and the available resources or capacity of an institution to provide that content through its faculty and structural characteristics (Darling-Hammond, 2000b).
Content
The knowledge base associated with early childhood teaching has changed rapidly in recent years. While teacher education programs have historically focused primarily on child development and the application of child development principles to curriculum and teaching, the current policy expectation that preschools become a part of formal schooling has created further demands. Therefore, policy recommendations concerning the preparation of early childhood teachers (see, e.g., Hyson, 2003; Katz & Goffin, 1990; McCarthy, 1990; Saracho & Spodek, 1983; Spodek & Saracho, 1990) propose that the training of students in teacher preparation programs include four general areas.
The first area is the foundation of early education, which includes child development and learning theory, as well as methods courses in both pedagogy and curricular approaches. In addition to knowledge of how children learn and general patterns of development, teachers need to facilitate learning across the content areas for diverse groupings of children. Therefore, the second area that teacher preparation programs should address is knowledge of the pedagogy involved in teaching young children literacy, math, social studies, science, and the arts. Third, to realize the kind of teaching practices and interactions among teachers and children that positively affect children's development and learning, teacher preparation programs also should "prepare teachers to understand how to apply this knowledge in specific program planning and in assessing and adapting instruction to meet the needs of individual children, especially those from diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds" (Bredekamp, 1996, p. 339). Finally, in order to be able to make use of the content they are learning in their coursework, preschool teachers need to have direct experience with young children in a variety of settings. Therefore, the current standards for early childhood teacher preparation advocated by the National Association for the Education of Young Children (Hyson, 2003) recommend that teachers participate in field experiences (observations, practica, and student teaching) where they can practice what they have learned (Hyson, 2003).
Despite these standards, only a few studies are available on what actually takes place within programs of preschool teacher preparation and whether they are able to address the needs of their students in these areas. In a nationally representative study of two- and four-year institutions of higher education, Early and Winton (2001) found that most early childhood teacher education programs currently in operation offer little, if any, coursework in linguistic and cultural diversity and the education of children with disabilities. Similarly, Ryan, Ackerman, and Song (2004), in their study of teachers' perceptions of their professional preparation, found that less than half of the 689 teachers interviewed felt that they were skilled to work with children with special educational needs or who were English-language learners. Further, Isenberg (2000) contends that early childhood teachers traditionally have not been prepared to teach domain-specific knowledge to young children, even though content standards in math, literacy, and science exist for 4-year-olds. Thus, a potential gap appears to exist between professional standards and the knowledge that teachers are learning in their programs of preparation.
Resources
The teaching of the curriculum in teacher education programs is reliant on the resources an institution provides to ensure that students are supported in their studies. Research into teacher education programs has demonstrated that intensive and personal interaction between faculty and students is a critical piece of becoming an early childhood teacher (Darling-Hammond, 2000a). The average early childhood educator is female, is approximately 39 years of age (Saluja, Early, & Clifford, 2002), and may only be starting her studies toward a bachelor's degree. To make sure that these nontraditional students do not take unnecessary classes, it is important that they receive adequate advisement. However, early childhood departments have a disproportionate number of part-time and adjunct faculty members, and as a result, the ratio of students to full-time faculty in early childhood education programs is 61 to 1 as opposed to 39 to 1 in higher education overall (Early & Winton, 2001). It is therefore not surprising that many teacher preparation programs across the United States report that one of their biggest challenges is responding to "the competing work and family responsibilities" of their students (Early & Winton, 2001, p. 297).
It is not just the number of faculty available to meet with students that is a concern. Also of concern is their ability to educate preschool teachers adequately for the task of teaching diverse groups of students for ongoing academic success. In their national study of two- and four-year institutions preparing early childhood teachers, Early and Winton (2001) found that only 53% of early childhood faculty had a degree in early childhood education or a related field, and only 64% had experience working with 3- or 4-year-olds.
In summary, although there are national standards determining what should be included in preparation programs for preschool teachers and some sense of the kinds of faculty resources needed to deliver such a curriculum, the limited research available suggests that most programs are not meeting these standards. The current research base focuses on teacher education programs already in operation, but what happens when a state gets the opportunity to develop a new set of teacher certification programs? Does the opportunity to create a system from the ground up mean that some of these gaps are addressed?
New Jersey has been involved in such a reform effort. This study examined whether increasing the education requirements for early childhood teachers in New Jersey led to a system of preparation that reflected national standards. Specifically, we sought to (1) map the current system of early childhood teacher preparation in New Jersey so that it was possible to determine what kinds of programs leading to certification are available to preschool teachers at various institutions, (2) determine the capacity of these programs to prepare a growing number of preschool teachers to meet the needs of the state, and (3) examine the content of the coursework to identify gaps that might exist between what the standards recommend preschool teachers need to know and be able to do and the programs available to teachers in New Jersey. Before outlining the methodology, we describe the context and shape of the reforms that have taken place in New Jersey's system of early childhood teacher preparation.
The New Jersey Context
New Jersey provides a unique context from which to explore the issue of preschool teacher certification and preparation because of the Abbott v. Burke (1998, 2000) Supreme Court decisions (Ryan & Ackerman, 2005). These decisions ruled that the 30 poorest districts, which came to be called Abbott districts, were to create systems of high-quality preschool for all 3- and 4-year-old children beginning in the 1999-2000 school year. The Abbott classrooms were to have a class size of no more than 15 students, with a certified teacher and teacher assistant per classroom. In addition, each program was required to use a developmentally appropriate curriculum linked to the state's core curriculum content standards and provide adequate facilities, special education, bilingual education, transportation, health, and other services as needed (Abbott v. Burke, 1998).
Since the public school system did not have the facilities or capacity to house all of the new preschool programs, the Abbott districts were allowed to contract with private child care centers and Head Start programs already offering preschool. In addition, to facilitate the implementation of developmentally appropriate curriculum, the Court recommended several empirically validated early childhood curriculum models. School districts created the leadership position of teacher consultant—or master teacher—to provide technical assistance, professional development, and mentoring to preschool teachers in implementing these curricula (Ryan, Hornbeck, & Frede, 2004).
Finally, to ensure high quality, the court also ruled that every publicly funded preschool classroom had to have a teacher with not only a bachelor's degree but also specialized training in early childhood education. This ruling immediately changed the landscape of early childhood education and teacher preparation in New Jersey.
Teachers who taught in New Jersey's public school preschool classrooms already had to have a bachelor's degree and a teaching certificate, and as long as they had two years of experience teaching preschool, they were grandfathered in. However, the majority of teachers in private child care classrooms were not qualified to teach under the new regulations. Prior to the Abbott ruling, in order to teach in most of the private centers in the state, teachers needed to have a minimum of a Child Development Associate (CDA) credential (Division of Youth and Family Services, 1998). Earning this credential involves undertaking 120 clock hours of training in such subjects as promoting a safe and healthy learning environment and supporting children's social and emotional development (Council for Professional Recognition, 2000). These teachers were now required to have the same qualifications as the public school preschool teachers—namely a bachelor's degree and specialized training—and they had to obtain the qualifications by September 2004. This requirement meant that large numbers of teachers were going to have to return to school.
In response to this mandate, New Jersey's institutions of higher education had to create specialized P-3 certification programs, utilizing both alternate route and traditional approaches to teacher preparation. Prior to the Abbott decision, early childhood teacher preparation at the state's four-year institutions of higher education was integrated with elementary programs that were designed to prepare teachers to work with children from preschool through middle school. Therefore, at the time of the Court decision, no programs were specifically designed to prepare teachers to work in preschool classrooms.
To facilitate implementation of the reforms required by the Abbott decision, the state government provided several funding sources (Quality and Capacity grants, Teacher Effectiveness and Teacher Preparation grants) through the Commission for Higher Education to help institutions of higher education expand their early childhood faculties. Moreover, a state-funded scholarship program was initiated to pay for teachers' tuition as they upgraded their qualifications. Thus a new system of early childhood teacher preparation was developed with the aim of producing a highly qualified workforce within four years.
Methodology
Sample
The sample for this study comprises 12 representatives from the total population of 14 institutions that provide early childhood teacher preparation in the state of New Jersey. Participants were selected in several steps. First, we identified all of the four-year institutions of higher education that provide teacher training in New Jersey. We then attempted to contact the individual responsible for early childhood programming at each of these institutions. In doing so, we discovered that 7 of them did not provide preschool teacher training. We then proceeded to make contact with a representative of the remaining 14 institutions to participate in a telephone interview. Twelve agreed to participate. Most of these individuals were faculty members responsible for coordinating early childhood programs in their respective institutions, although one was a P-3 academic advisor, and two were directors of teacher education. Therefore, 85% of the four-year institutions offering preschool teacher training in New Jersey were represented in the final sample for this study.
Data Collection
All participants were interviewed via telephone during 2003-2004 using a semi-structured protocol developed by the authors (Lobman, Ryan, & Ackerman, 2003). The protocol was field tested with key informants who had knowledge of the four-year colleges and universities. These individuals were not included in the final sample. Utilizing the work of Early and Winton (2001); Horm-Wingerd, Hyson, and Karp (2000); and Isenberg (2000), the protocol was structured under four main topics. We wanted to determine the content of training offered in P-3 programs, the current capacity of institutions, and the resources available to support students. In addition, the protocols elicited basic contact and program information that could be used to develop an online directory of early childhood teacher preparation options.
Interviews were administered by members of the research team or a trained research assistant. Prior to the interview, each participant received a list of information that he or she would need to have available to answer the questions. Interviews lasted from 30 to 60 minutes. When a participant was unable to answer a question because of lack of information, a follow-up call was made at a later date to complete the interview. During the interviews, all responses were recorded manually on a recording form and were then entered into an SPSS database as soon as possible after the interview was completed.
Data Analysis
Analysis of the data set followed a three-step plan. First, descriptive statistics were collected to provide a portrait of each kind of training institution in terms of capacity, programs offered, content of trainings and supports, and challenges to offering P-3 teacher certification programs. Second, inferential statistics (e.g., exact tests) were used to examine the relationships between various institutional characteristics and the content being offered to preschool teachers. Finally, the findings of this study were then compared to professional standards (Hyson, 2003) and the one national study (Early & Winton, 2001) of early childhood teacher preparation programs.
Limitations
The data presented in this study were collected using self-report of participants who worked within the teacher preparation system. The participants were selected based on available information about which individuals would be most likely to have an overall knowledge of the early childhood teacher preparation programs at the various colleges. However, self-report data can be somewhat unreliable because there is no guarantee that what is reported is completely accurate. In addition, it is not possible, given the limitations of a survey, to determine how much preparation teachers are actually receiving in specific topics. Exploring these aspects further would require an examination of syllabi, interviews with instructors, and observations of classes.
Findings
The findings are presented according to each of our purposes. We begin with the different programs leading to certification, followed by examination of the resources available at universities preparing early childhood teachers. Finally, we explore the content of the coursework that students are required to take in order to obtain a P-3 certificate. Where relevant, comparisons between these findings and the national context are also made.
Routes to Certification
Two main pathways lead to teacher certification in New Jersey. The first of these is the traditional route of preparation, resulting in a bachelor's or master's degree and certification. Most of the bachelor's-level programs involve 30 credits in educational methodology courses, as well as a 30-credit academic major and approximately 60 additional credits of liberal arts coursework. The 30 credit hours in educational methodology are to include the study of behavioral/social sciences, the teaching of literacy and numeracy, and the education of special needs and linguistically diverse students. The coursework should also be aligned with the Professional Standards for Teachers (N.J.A.C. 6A:9-10.2). Traditional teacher education students also participate in observational field experiences and semester-long student teaching internships. Traditional teacher education programs are available at the undergraduate and the post-baccalaureate levels.
All of the 12 colleges and universities offer a traditional route program leading to a P-3 credential. These programs are further subdivided into stand-alone P-3 programs and those that prepare students to receive a dual P-3/K-8 certificate. The majority of schools have chosen to develop dual certification programs that prepare graduates to work in either an elementary or a preschool setting. One school offers only a P-3 endorsement program, in which holders of other teaching certificates (i.e., K-8 certificate) take a set of courses that will allow them to teach in an Abbott preschool.
New Jersey has also had alternate route certification since 1985 and a specialized P-3 alternate route program since 2001. In the P-3 alternate route program, teachers who are already employed as preschool teachers in an Abbott district must enroll in for-credit coursework in P-3 pedagogy in a state-approved alternate route program. They also receive 34 weeks of mentoring. Over half of the schools (58%) offer alternate route P-3 programs in addition to a traditional route program.
There are 43,000 children eligible for preschool in the Abbott districts, and 2,900 qualified teachers are needed to educate them. Findings from this study indicate that teacher preparation programs are producing enough teachers to meet this demand (see Fig. 1). At the time of our survey, approximately 2,500 students were enrolled in approved P-3 certification programs. The majority of these students (58%) are participating in traditional four-year undergraduate certification programs—in either a stand-alone P-3 (37%) or a dual P-3/K-8 (21%) program. An additional 24% who are employed in an Abbott preschool are enrolled in one of the seven state-approved alternate route programs. The remaining students are enrolled in various post-baccalaureate programs that include endorsement programs for teachers who hold a nonpreschool teaching certificate and preservice certification programs.
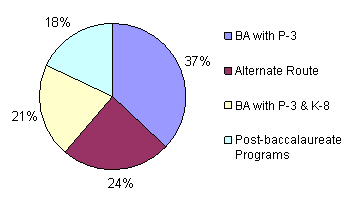
Figure 1. Student enrollment in certification programs.
Resources
Because one of the aims of this study was to determine the capacity of institutions to meet the demand for qualified preschool teachers within the state, we asked participants a series of questions concerning various institutional resources related to faculty and student supports as well as challenges facing institutions of higher education.
Faculty. National research shows that most teacher education programs have difficulty finding and keeping faculty that have specialized knowledge and experience in preschool education (Early & Winton, 2001). Seventy-five full-time early childhood faculty members employed at the 12 universities participated in the study, and 50% of them were tenured. In addition to full-time faculty, 87 part-time and adjunct early childhood teacher educators participated, making a total of 162 faculty members teaching in early childhood programs in these 12 institutions. The early childhood faculty in New Jersey's four-year institutions of higher education is highly qualified to prepare early childhood teachers—75% of them have a degree in early childhood or a related field, and 82% have had direct employment experience with 3- and 4-year-olds. All faculty members have a minimum of a master's degree, and 49% hold a doctorate. In addition, over half of the full-time early childhood faculty is tenured, providing a stable base from which to continue to build these programs.
Consistent with national averages, 67 of the 75 full-time faculty members are White (81%), while only 8 are African American (11%), 5 are Asian American (7%), and 1 is Latina (1%). The diversity of the faculty is slightly greater when the calculations include both part-time and adjunct faculty. However, 5 of the 12 schools have early childhood faculties that are entirely White.
New Jersey programs have lower student-to-faculty ratios and more qualified faculty than early childhood teacher preparation programs nationwide. Although the average student-to-faculty ratio in early childhood programs nationwide is 61 to 1, in New Jersey, it is 43 to 1—much closer to the national average of 39 to 1 for higher education as a whole (Early & Winton, 2001). Although the statistics statewide look promising, significant variation exists across the 12 institutions, ranging from 1 full-time faculty member to every 8 students at the one institution to 1 faculty member to every 156 students at another. When faculty resources were examined in relation to institutional size and programs offered, no statistical differences were found.
Student Supports. Many of the preschool teachers who are trying to upgrade their qualifications in response to the Abbott 2000 court decision are nontraditional students. In a recent study of this population, Ryan and Ackerman (2005) found that the average age of inservice teachers in New Jersey is 38 years, and most have been working in preschool education for an average of 9 years. Because many of these students work full time, they may require flexibility in class times and locations. Similarly, they may need special academic supports because of their lack of familiarity with university settings.
Ten of the 12 four-year colleges and universities that participated in this study provide some kind of support to their students who are enrolled in P-3 programs. Nearly 60% of the schools offer classes on-site at local school districts, and 33% hold classes at community-based child care centers. Similarly, 55% of universities offer classes at satellite facilities in local communities, and 18% offer classes online. Because many students currently enrolled in P-3 programs are already employed in preschools, 7 of the 12 colleges and universities allow their students to complete all of their student teaching requirements at their place of employment. A quarter of the universities offer access to follow-up professionals, and more than half (60%) of the universities offer mentoring assistance that is not related to coursework.
Challenges. National research suggests that most institutions of higher education do not have the infrastructure to adequately meet the demand for preschool teachers (Early & Winton, 2001; Isenberg, 2000). Because P-3 programs have expanded quickly to meet the requirements of Abbott, we asked a series of questions in order to determine the current gaps in the infrastructure. The two largest challenges (see Table 1) are a lack of full-time faculty and enough physical space to accommodate the number of students seeking coursework in early childhood. At the same time, these same two resources were not considered a barrier to delivering programs by approximately half of the institutions.
| Challenges | Large Challenge | Somewhat of a Challenge | Not a Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lack of classroom space on campus | 42% | 0% | 58% |
| Lack of full-time early childhood faculty | 33% | 25% | 42% |
| Recruiting early childhood faculty | 25% | 17% | 58% |
| Quality of student teaching placements | 25% | 33% | 42% |
| Quantity of student teaching placements | 8% | 0% | 92% |
| Support from institution | 25% | 25% | 50% |
When we examined these challenges via size of institution, no significant differences were found. Since no evidence suggests that these challenges were related to institutional characteristics, it would seem that variability exists in the resources available to P-3 preparation programs.
Content
As mentioned previously, the research literature suggests that in order to teach young children effectively preschool teachers need three broad areas of knowledge, including early childhood foundations, domain-specific curriculum content, and issues related to working with families and working with students from diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds. Institutions were asked to identify from a list of topics the content of the coursework constituting their P-3 programs in each of these areas and indicate whether the content constituted an entire required class, was part of a required class, or was not required at all. In addition, since practical experiences are considered an integral part of teacher preparation, participants were asked about the practica (short-term placements) and student teaching experiences required by their programs. Because 7 institutions offer both a traditional and alternate route program, and these two routes have different requirements, the data presented below include answers regarding all 19 programs (12 traditional and 7 alternate route programs).
Figure 2 provides information on coursework that is considered foundational to early childhood teaching—including child development, classroom management, early childhood curriculum, developmentally appropriate practice, play, assessment, and philosophical and theoretical foundations of early childhood education. P-3 students in all but one program receive at least one entire course in child development. Seventeen programs (89%) devote an entire class to curriculum development. Philosophical and theoretical foundations and developmentally appropriate practice (DAP) are also well represented, with 100% of the programs offering these topics as either part or all of a required class. On the other hand, several programs do not cover play, assessment/evaluation, or classroom management—all of which one could consider critical to the contemporary preschool environment (Bredekamp & Copple, 1997).
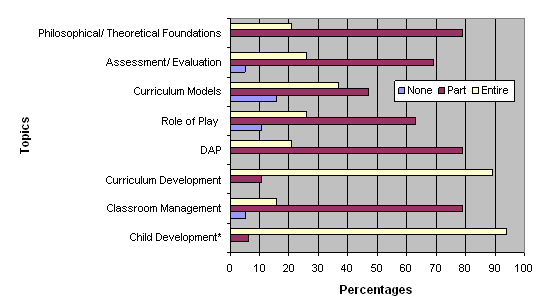
Figure 2. Early childhood foundations
(*18 out of 19 universities responded to this
question).
Increasingly, preschool teachers are expected to scaffold children's learning in domain-specific knowledge and therefore need to know the methodology and concepts appropriate for 3- and 4-year-old children. As can be seen in Figure 3, the majority of schools offer some coursework in all of the domains. The topic covered most by far is literacy. Fifteen P-3 programs (79%) across the state offer literacy as a stand-alone class. On the other hand, no more than four programs (21%) require a full class in any of the other content areas, and several schools require no coursework in teaching social studies, math, music, and art.
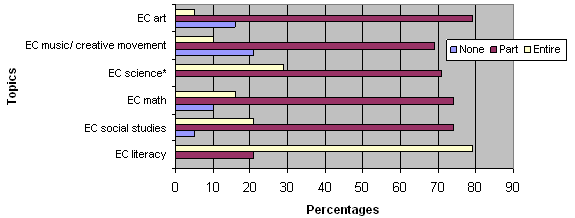
Figure 3. Specific-content areas
(*only seven of the universities were asked this
question).
Participants in the study were asked about coursework that prepares students to work with diverse student populations (see Fig. 4). Only seven (38%) of the programs require their students to take an entire class on working with children with special needs, and three programs (16%) offer no coursework on this topic. Furthermore, only two programs (11%) require a full class on working with children whose first language is not English, and, again, four programs (20%) do not address this topic at all. On the other hand, almost all of the programs (95%) provide some preparation for working with families.
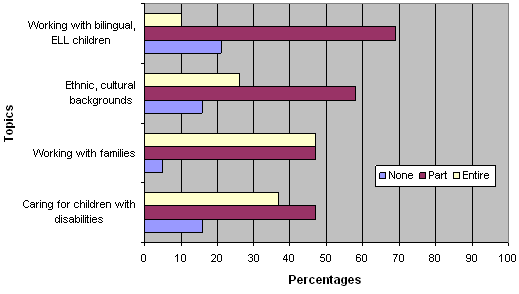
Figure 4. Diversity.
To determine the type of preparation that students were given in these content areas, the colleges were asked whether a practicum experience was connected to the coursework for particular topic areas. Only three topics—curriculum development, developmentally appropriate practice, and literacy—had a required practicum experience in over 50% of the schools. On the other hand, play, music, art, science, working with families, and working with English-language learners were connected to a practicum experience in less than 25% of the schools. Finally, all of the traditional route programs required a full-time student teaching placement in at least one early childhood setting. A third of the schools indicated that students were placed in two settings as part of their student teaching experience.
The content being offered across the 12 colleges and universities was examined in relation to various institutional and programmatic characteristics. Significant differences were found for route of preparation. Students in alternate route programs are less likely to receive coursework in the areas of math (p < .05), play (p < .05), and early childhood assessment methods (p < .05) than are students in traditional route programs.
In summary, when compared to national standards, the state's P-3 preparation programs appear to be providing the content that research shows is needed for the preparation of high-quality preschool teachers. Many of the programs we surveyed include comprehensive coursework in all three recommended categories—foundations, domain-specific knowledge and pedagogy, and diversity. However, these somewhat promising findings notwithstanding, some serious concerns still remain about the content of the programs in New Jersey. Despite recommendations highlighting the importance of coursework in domain-specific pedagogy, teachers are still receiving substantially more coursework in child development, general early childhood curriculum, and literacy than they are in math, science, and social studies.
Moreover, despite having been created in the past five years, and having access to the most current research, New Jersey programs appear not to compare well with a national sample in the area of diversity training (Early & Winton, 2001). Whereas nationwide 60% of early childhood teacher preparation programs require students to take a full course in working with children with disabilities, in New Jersey only 30% of the schools currently require such a class. Similarly, whereas nationwide 43% of programs require a full course on working with children and families from diverse cultural and linguistic backgrounds, in New Jersey only 28% of schools currently require such a course. While the findings from the current study did indicate that many of New Jersey's schools offered these topics as part of a required class, it is clear that New Jersey mirrors the rest of the country in providing less coursework in the area of diversity than in other subject areas.
Discussion
The findings from this study indicate that it is possible, in a relatively short period of time, to put in place a system of early childhood teacher preparation that has the capacity to upgrade the credentials of the state's workforce. Although the court mandate catalyzed the state into action, two interrelated factors appear to contribute to making this reform possible.
The first of these was the existence of early childhood leadership and advocacy within the state. Prior to the mid-1980s, the state had a Nursery/Kindergarten certificate, and many faculty members working in New Jersey colleges at the time of Abbott had previously taught in these programs. Consequently, faculty members in New Jersey were experts in early childhood education, but they had spent many years working within the K-5 teacher preparation system. Most of these faculty members were active through the New Jersey chapter of the Association of Early Childhood Teacher Educators (NJAECTE). Therefore, when the need arose to create a new specialized P-3 teaching credential, a group of faculty with expertise was available as well as an organization that could help lead and facilitate this process. This preexisting leadership played an important role in the ability of schools of higher education to quickly mobilize in response to the court mandate.
A second major factor in the success of these policy changes in New Jersey is that the initiative received the necessary financial resources to be able to offer P-3 programs. The state made available two kinds of grants—the Teaching Effectiveness and Teacher Preparation Grant and the Quality and Capacity Grant—that were specifically targeted for the hiring of faculty in areas of need, including early childhood. Therefore, institutions of higher education were able to expand their early childhood faculties and as a consequence their capacity to meet the demand for qualified preschool teachers.
Although New Jersey had the leadership and resources to produce a system of early childhood teacher preparation, the findings of this study indicate that gaps still exist between national standards and current practices in New Jersey's institutions of higher education. It is both the successes and the limitations of New Jersey's efforts to create a system of early childhood teacher preparation that can inform other states' initiatives.
Clearly, a good starting point for any state is to capitalize on the leadership and wisdom available within the early childhood community. The field of early childhood has had a long history of advocacy and leadership at local, state, and national levels as is evidenced by the influence of the National Association for the Education of Young Children on early childhood practice and policy. It would seem sensible for states to begin contacting and working with individuals within these organizations as a way to bring stakeholders into the debate and harness their expertise and commitment to the education of the teachers of young children.
At the same time, it is important to go beyond the available expertise to ensure that programs meet the most current standards. Although New Jersey had a cohort of early childhood faculty members who were working together in this reform effort, the fact remains that many of the programs do not address all of the content deemed to be necessary for teaching young children. One possible reason is that many faculty members currently working in institutions of higher education do not have the up-to-date knowledge needed for the state's current social, political, and economic context. For example, special education and teaching English-language learners have traditionally been separate areas of education, and faculties were not expected to be able to incorporate these topics into their curriculum and child development classes. Therefore, policy makers will need to evaluate the expertise of current faculty in order to determine their professional development needs in these areas. Although such training cannot be a one-size-fits-all approach, some oversight across institutions will be necessary to ensure that no matter where students receive their training they will encounter the necessary content.
Any state embarking on this type of reform will need to provide financial resources to ensure that institutions of higher education can recruit faculty and increase their capacity to prepare qualified teachers. However, the results of this study would indicate that some consideration must be given to the form of the financial support that is provided to teacher preparation programs. In the case of New Jersey, grants enhanced the ability of institutions to hire new faculty, but they also may have led to the dramatic variability that was found in student-to-faculty ratios among institutions. Grants are a notoriously unstable method of funding, which can lead some schools to rely on part-time and adjunct faculty. Because the research indicates that faculty-student relations are critical to nontraditional students succeeding in teacher preparation programs, policy makers should consider a more permanent financial commitment for the development of programs.
In conclusion, developing a high-quality system of teacher preparation requires the coordination of human and financial resources so that there is equity and quality in the programs offered by institutions within a state. This coordination is particularly critical in preschool education because the workforce is extraordinarily diverse in qualifications, knowledge, and experience, and the workforce is located in a range of settings that have historically been regulated differently. As the New Jersey context has indicated, most states probably have the leadership and much of the expertise needed to develop high-quality programs, but without coordination and support, it is unlikely that states will be able to transform the early childhood workforce in the way that research indicates is necessary. In short, the potential for creating a high-quality system is there—it is now up to teacher educators and policy makers to work together to make it happen.
Acknowledgment
The research for this article was made possible by a grant from the Foundation for Child Development.
References
Abbott v. Burke, 153 N.J. 480 (1998). Retrieved February 24, 2011, from http://lawlibrary.rutgers.edu/decisions/supreme/a-155-97.opn.html
Abbott v. Burke, 163 N.J. 95 (2000). Retrieved February 24, 2011, from http://lawlibrary.rutgers.edu/courts/supreme/m-1336-98.opn.html
Ackerman, Debra J. (2004). States' efforts in improving the qualifications of early care and education teachers. Educational Policy, 18(2), 311-337. EJ 690 085.
American Association of Colleges for Teacher Education (AACTE) Focus Council on Early Childhood Education. (2004). The early childhood challenge: Preparing high-quality teachers for a changing society. Washington, DC: AACTE. ED 484 660.
Barnett, W. S. (2003, March). Better teachers, better preschools: Student achievement linked to teacher qualifications. Preschool Policy Matters, 2. ED 480 818.
Barnett, W. Steven. (1998). Long-term effects on cognitive development and school success. In W. Steven Barnett & Sarane Spence Boocock (Eds.), Early care and education for children in poverty: Promises, programs, and long-term results (pp. 11-44). Albany: State University of New York Press. ED 417 265.
Bowman, Barbara T.; Donovan, M. Suzanne; & Burns, M. Susan (Eds.). (2001). Eager to learn: Educating our preschoolers. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. ED 447 963.
Bredekamp, Sue. (1996). Early childhood education. In John Sikula, Thomas Buttery, & Edith Guyton (Eds.), Handbook of research on teacher education (pp. 323-347). New York: Macmillan. ED 400 230.
Bredekamp, Sue, & Copple, Carol (Eds.). (1997). Developmentally appropriate practice in early childhood programs serving children from birth through age 8. (Rev. ed.). Washington, DC: National Association for the Education of Young Children. ED 403 023.
Campbell, Frances A.; Pungello, Elizabeth P.; Miller-Johnson, Shari; Burchinal, Margaret; & Ramey, Craig T. (2001). The development of cognitive and academic abilities: Growth curves from an early childhood educational experiment. Developmental Psychology, 37(2), 231-242. EJ 628 465.
Council for Professional Recognition. (2000). The Child Development Associate national credentialing program: Making a difference in the early care and education of young children. Washington, DC: Author.
Darling-Hammond, Linda. (2000a). Solving the dilemmas of teacher supply, demand, and standards: How we can ensure a competent, caring, and qualified teacher for every child [Online]. New York: National Commission on Teaching & America's Future. Available: http://www.nctaf.org/documents/supply-demand-standards.pdf [2006, October 5]. ED 463 337.
Darling-Hammond, Linda. (Ed.). (2000b). Studies of excellence in teacher education: Preparation in a five-year program. Washington, DC: AACTE Publications. ED 468 995.
Division of Youth and Family Services, Department of Human Services, & State of New Jersey. (1998). Manual of requirements for child care centers. Trenton, NJ: Bureau of Licensing.
Dwyer, M. Christine; Chait, Robin; & McKee, Patricia. (2000). Building strong foundations for early learning: Guide to high-quality early childhood education programs. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education, Planning and Evaluation Service. ED 448 905.
Early, Diane M., & Winton, Pamela J. (2001). Preparing the workforce: Early childhood teacher preparation at 2- and 4-year institutions of higher education. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 16(3), 285-306. EJ 637 860.
Horm-Wingerd, Diane; Hyson, Marilou; & Karp, Naomi. (2000). Introduction. In New teachers for a new century: The future of early childhood professional preparation (pp. 1-15). Washington, DC: National Institute on Early Childhood Development and Education, U.S. Department of Education. ED 438 954.
Howes, Carollee. (1997). Children's experiences in center-based care as a function of teacher background and adult:child ratio. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 43(3), 404-425. EJ 554 324.
Hyson, Marilou. (Ed.). (2003). Preparing early childhood professionals: NAEYC's standards for programs. Washington, DC: National Association for the Education of Young Children.
Isenberg, Joan P. (2000). The state of the art in early childhood professional preparation. In New teachers for a new century: The future of early childhood professional preparation (pp. 17-58). Washington, DC: National Institute on Early Childhood Development and Education, U.S. Department of Education. ED 438 954.
Katz, Lilian G., & Goffin, Stacie G. (1990). Issues in the preparation of teachers of young children. In Bernard Spodek & Olivia N. Saracho (Eds.), Yearbook in early childhood education, Vol. 1: Early childhood teacher preparation (pp. 192-208). New York: Teachers College Press.
Lobman, Carrie; Ryan, Sharon; & Ackerman, Debra J. (2003). Survey of early childhood teacher preparation at New Jersey's four-year colleges and universities. New Brunswick: Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey.
McCarthy, Jan. (1990). The content of early childhood teacher education programs: Pedagogy. In Bernard Spodek & Olivia N. Saracho (Eds.), Yearbook in early childhood education, Vol. 1: Early childhood teacher preparation (pp. 82-101). New York: Teachers College Press.
Professional Standards for Teachers (N.J.A.C. 6A) [Online]. Available: http://www.state.nj.us/njded/code/current/title6a/chap9.pdf#page=7 [2005, October 12].
Ryan, Sharon, & Ackerman, Debra J. (2005). Using pressure and support to create a qualified workforce. Education Policy Analysis Archives [Online], 13(23). Available: http://epaa.asu.edu/epaa/v13n23/ [2006, October 5].
Ryan, Sharon; Ackerman, Debra J.; & Song, Hao. (2004). Getting qualified and becoming knowledgeable: Preschool teachers' perspectives on their professional preparation. Manuscript in preparation.
Ryan, Sharon; Hornbeck, Amy; & Frede, Ellen. (2004). Mentoring for change: A time use study of teacher consultants in preschool reform. Early Childhood Research & Practice [Online], 6(1). Available: http://ecrp.uiuc.edu/v6n1/ryan.html [2005, October 5].
Saluja, Gitanjali; Early, Diane M.; & Clifford, Richard. (2002). Demographic characteristics of early childhood teachers and structural elements of early care and education in the United States. Early Childhood Research & Practice [Online], 4(1). Available: http://ecrp.illinois.edu/v4n1/saluja.html [2005, April 3]. ED 464 765.
Saracho, Olivia N., & Spodek, Bernard. (1983). Preparing teachers for bilingual/multicultural classrooms. In Olivia N. Saracho & Bernard Spodek (Eds.), Understanding the multicultural experience in early childhood education (pp. 125-146). Washington, DC: National Association for the Education of Young Children. ED 238 560.
Spodek, Bernard, & Saracho, Olivia N. (1990). Preparing early childhood teachers. In Bernard Spodek & Olivia N. Saracho (Eds.), Yearbook in early childhood education, Vol. 1: Early childhood teacher preparation (pp. 23-44). New York: Teachers College Press.
Whitebook, Marcy. (2003). Bachelor's degrees are best: Higher qualifications for pre-kindergarten teachers lead to better learning environments for children. Washington, DC: Trust for Early Education.
Author Information
Carrie Lobman is assistant professor of elementary and early childhood education at Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey. Dr. Lobman's research interests include play, a performatory approach to human development, and early childhood teacher education and professional development.
Carrie Lobman
Department of Learning and Teaching
Graduate School of Education
Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey
10 Seminary Place
New Brunswick, NJ 08901
Telephone: 732-932-7496, ext. 8116
Email: lobman@rci.rutgers.edu
Sharon Ryan is associate professor of early childhood education at Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey. Dr. Ryan's research interests include early childhood curriculum and policy, early childhood teacher education, and the potential of critical theories for rethinking early childhood practices.
Sharon Ryan
Department of Learning and Teaching
Graduate School of Education
Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey
10 Seminary Place
New Brunswick, NJ 08901
Telephone: 732-932-7496, ext. 8114
Email: sr247@rci.rutgers.edu
Jill McLaughlin is an elementary teacher at Nishuane Elementary, Montclair Public School District, who is interested in educational policy and professional development for teachers.
Jill McLaughlin
Montclair Public School District
Nishuane Elementary
32 Cedar Ave.
Montclair, NJ 07042
Telephone: 973-509-4222
Email: jmclaughlin@montclair.k12.nj.us

